Drug Repurposing Study Explores ACE2 Modulation for COVID-19 Therapeutics
🧠 Introduction
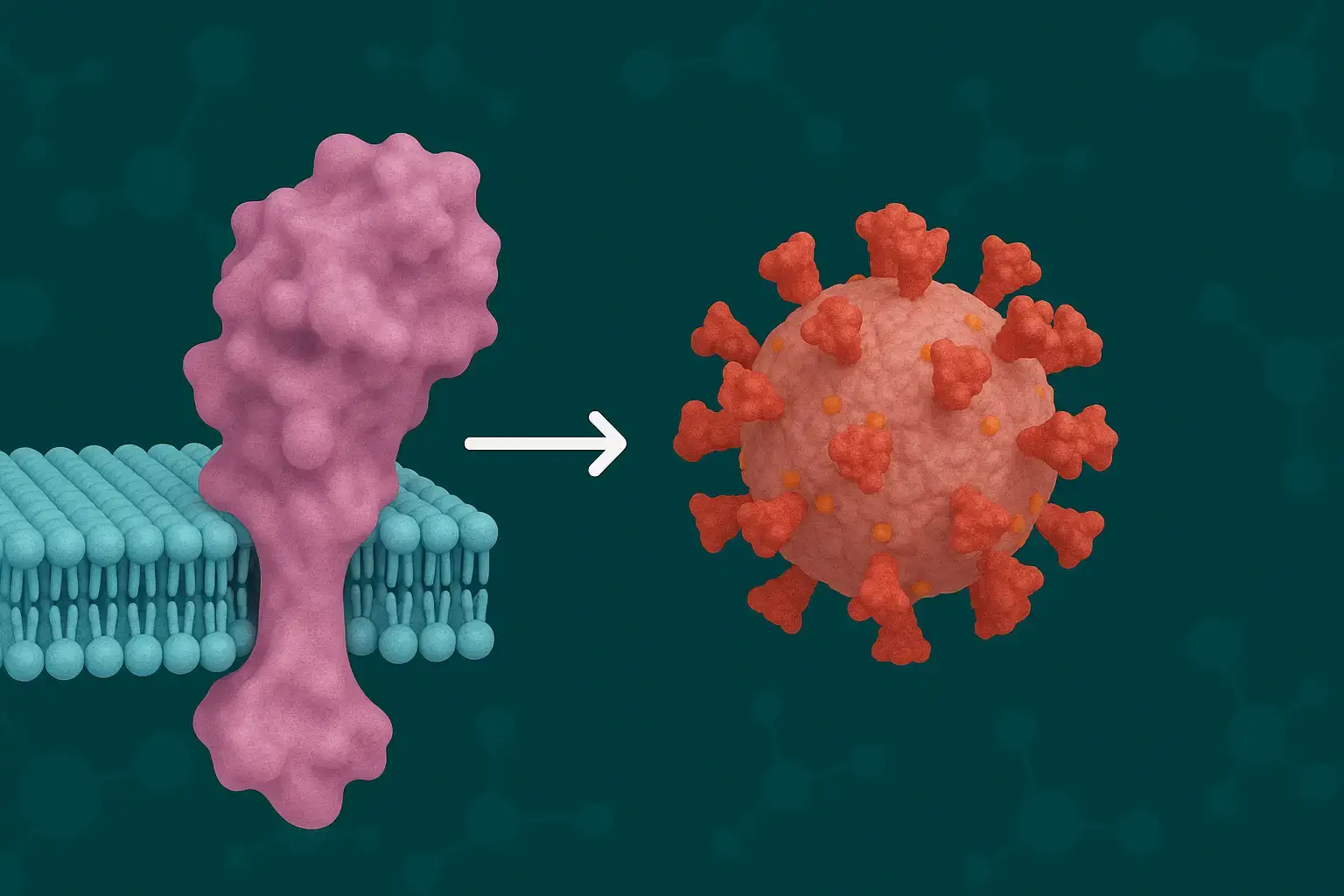
ACE2 is best known as the entry receptor for SARS-CoV-2, the virus behind COVID-19. But it also plays critical roles in cardiovascular and renal physiology. In our latest study, published in Biomolecules, we evaluated how different drugs affect the maturation and cellular trafficking of ACE2—revealing both risks and therapeutic possibilities.
🔍 Research Summary
We set out to understand how ACE2 is processed and transported within cells—and how drug candidates might alter this process. Using biochemical and cellular assays, we evaluated the impact of 23 different compounds on ACE2’s maturation and localization.
Key findings include:
- ACE2 maturation is typically fast and efficient under normal conditions.
- Eight of the tested compounds significantly reduced ACE2 maturation levels.
- Three compounds led to an approximate 20% reduction.
- While trafficking inhibitors had notable effects, most proposed COVID-19 drugs showed only mild impact—and statins had no observable effect.
These results suggest that modifying ACE2 expression and localization is possible, but must be done with precision, given its dual role in normal physiology and viral infection.
🌍 Broader Impact
This research adds valuable knowledge to the ongoing search for COVID-19 therapeutics, especially those based on drug repurposing. It also highlights a nuanced reality: targeting host factors like ACE2 can be a double-edged sword. While reducing ACE2 availability might block viral entry, it could also disrupt its protective functions in organs.
📎 Reference
@article{Alkhofash2024,
title = {The Evaluation of Drugs as Potential Modulators of the Trafficking and Maturation of ACE2, the SARS-CoV-2 Receptor},
journal = {Biomolecules},
volume = {14},
number = {7},
year = {2024},
issn = {2218-273X},
doi = {https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14070764},
url = {https://www.mdpi.com/2218-273X/14/7/764},
author = {Alkhofash, Nesreen F. and Ali, Bassam R.}
}


اترك تعليقاً